ketoacidosis pathophysiology Medicowesome: pathophysiology: diabetic ketoacidosis
Have you ever heard of Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)? It is a serious complication of diabetes that can be life-threatening if not treated promptly. Recently, I came across some PowerPoint slides and images that explain the pathophysiology of DKA. I found them quite informative and thought of sharing some key points with you.
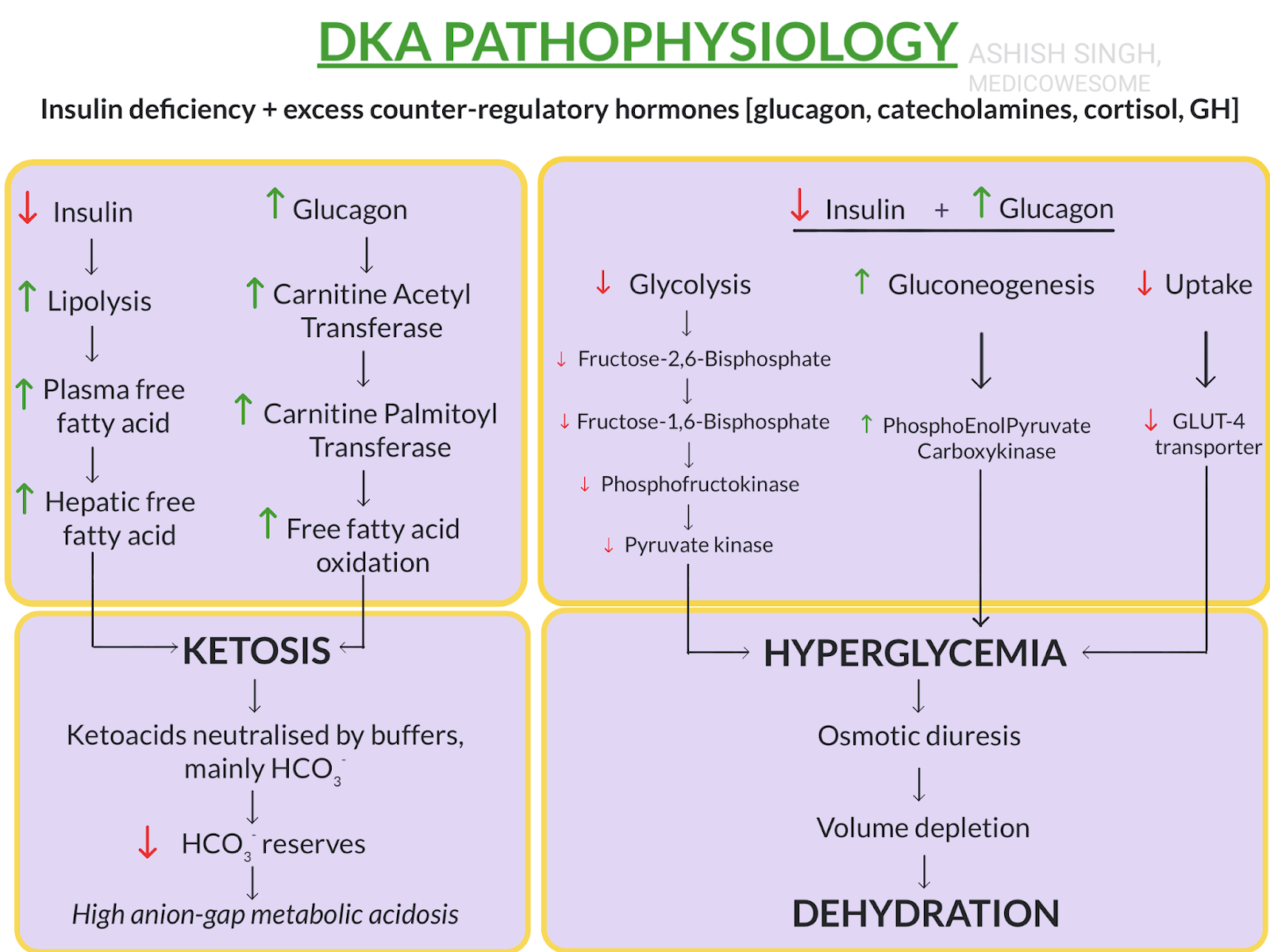
Pathophysiology of DKA
_1541410883_40244-7.jpg) DKA is characterized by the presence of high blood sugar levels, an excess of ketone bodies, and metabolic acidosis. It occurs when there is an absolute or relative deficiency of insulin, which leads to a shift in metabolism from glucose to fatty acids. As a result, ketone bodies are produced, which in turn results in an increase in the acidity of the blood. This condition is further exacerbated by dehydration, which is a common feature in patients with DKA.
DKA is characterized by the presence of high blood sugar levels, an excess of ketone bodies, and metabolic acidosis. It occurs when there is an absolute or relative deficiency of insulin, which leads to a shift in metabolism from glucose to fatty acids. As a result, ketone bodies are produced, which in turn results in an increase in the acidity of the blood. This condition is further exacerbated by dehydration, which is a common feature in patients with DKA.
There are various factors that can trigger DKA, such as infections, missed insulin doses, trauma, and surgery. In addition, certain medications, such as glucocorticoids and diuretics, can also contribute to DKA.
Signs and Symptoms of DKA
 The classic signs and symptoms of DKA include excessive thirst, frequent urination, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, fruity breath, and confusion. In severe cases, patients may experience seizures, coma, and even death. Therefore, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention if you suspect DKA.
The classic signs and symptoms of DKA include excessive thirst, frequent urination, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, fruity breath, and confusion. In severe cases, patients may experience seizures, coma, and even death. Therefore, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention if you suspect DKA.
Treatment of DKA
The treatment of DKA typically involves a combination of insulin therapy, fluid replacement, and electrolyte replacement. Insulin is administered to help lower blood sugar levels and prevent the production of ketone bodies. Fluid replacement is necessary to correct dehydration, and electrolyte replacement is needed to correct any imbalances in the blood. In severe cases, hospitalization may be required, and continuous monitoring of blood glucose, electrolyte levels, and acid-base status is crucial.
In conclusion, DKA is a severe complication of diabetes that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment. Understanding the pathophysiology of DKA and being aware of the signs and symptoms can help prevent life-threatening complications. Therefore, if you or anyone you know has diabetes, it is imperative to maintain good blood sugar control and seek medical attention if you suspect DKA.
If you are looking for Medicowesome: Pathophysiology: Diabetic Ketoacidosis you’ve visit to the right web. We have 5 Pics about Medicowesome: Pathophysiology: Diabetic Ketoacidosis like Pathogenesis and Pathophysiology of Diabetic Ketoacidosis | GrepMed, Medicowesome: Pathophysiology: Diabetic Ketoacidosis and also Aldosterone In Dka | DiabetesTalk.Net. Read more:
Medicowesome: Pathophysiology: Diabetic Ketoacidosis
 www.medicowesome.comketoacidosis pathophysiology diabetic dka summary happens
www.medicowesome.comketoacidosis pathophysiology diabetic dka summary happens
Pathogenesis And Pathophysiology Of Diabetic Ketoacidosis | GrepMed
 www.grepmed.compathophysiology ketoacidosis diabetic dka diabetes pathogenesis dm pathophys grepmed
www.grepmed.compathophysiology ketoacidosis diabetic dka diabetes pathogenesis dm pathophys grepmed
Aldosterone In Dka | DiabetesTalk.Net
 diabetestalk.netketoacidosis diabetic diabetes type ketosis pediatric dka starvation population insulin symptoms figure signs aldosterone diabetestalk quizlet sign
diabetestalk.netketoacidosis diabetic diabetes type ketosis pediatric dka starvation population insulin symptoms figure signs aldosterone diabetestalk quizlet sign
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) - PowerPoint Slides
_1541410883_40244-7.jpg) www.myprivatetutor.mydka ketoacidosis diabetic pathophysiology powerpoint
www.myprivatetutor.mydka ketoacidosis diabetic pathophysiology powerpoint
Pathophysiology Of Diabetic Ketoacidosis : Animation ~ MedchromeTube
 tube.medchrome.comketoacidosis pathophysiology diabetic diagram dka diabetes animation mechanism coma diagnostic tests diabetestalk accuracy a1c walgreens test glucose blood ph
tube.medchrome.comketoacidosis pathophysiology diabetic diagram dka diabetes animation mechanism coma diagnostic tests diabetestalk accuracy a1c walgreens test glucose blood ph
Ketoacidosis diabetic diabetes type ketosis pediatric dka starvation population insulin symptoms figure signs aldosterone diabetestalk quizlet sign. Ketoacidosis pathophysiology diabetic dka summary happens. Diabetic ketoacidosis (dka)